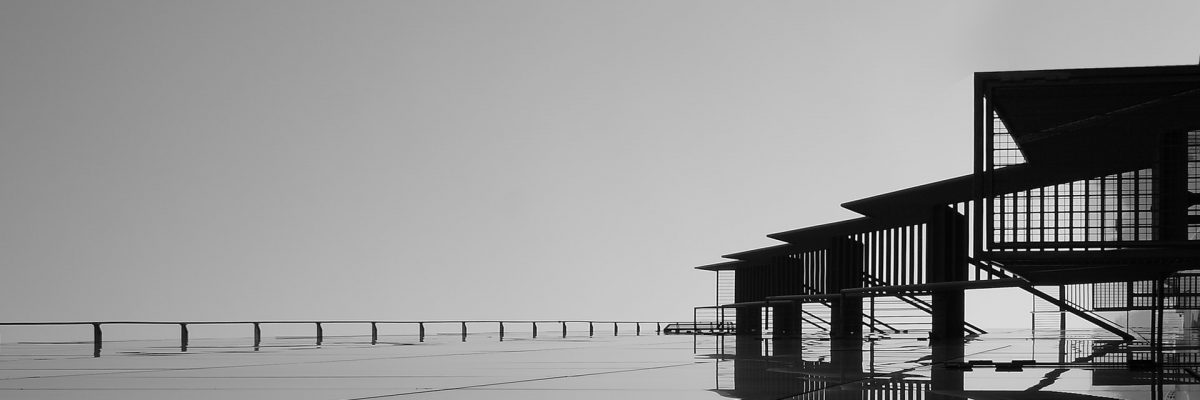
A flat roof is one of the 3 types of roofing in home design, with a sloping roof and the rounded roof.
The flat roof differs because it is made up of a single section and is presented as a terrace. The structure also differs in that it is not a frame but a kind of support (load-bearing element).
A flat roof consists of several elements:
The waterproof coating: placed on the surface prevents water from penetrating the structure of the flat roof and the house.
– A vapour barrier that protects the insulation from moisture.
– The thermal insulation: to insulate your flat roof from both heat and cold.
– An independence screen, possibly to separate incompatible chemical elements.
– Openings to let light in and ventilate.
The different types of flat roofs
The flat roof is very slightly sloping. It can, therefore, be used as an outdoor living space, accessible from the upper floor: it is then called a roof terrace. However, this is not always the case, as the flat roof is not always accessible.
There are 2 main types of flat roofs:
– Accessible flat roof: covered with wood, concrete, stone, tiles or about 30 cm of earth.
– Inaccessible” flat roof: accessible only for the maintenance of the roof or installations present on the top (mechanical ventilation, smoke evacuation ducts, etc.), and for waterproofing.
Support materials
The flat roof is surrounded by support which fulfils the same role as the roof structure (for a sloping roof, for example).
The 3 primary materials for the support of this roof are:
– Masonry
It is then mainly a solid slab:
◦ in concrete;
◦ in composite material;
◦ with steel reinforcements: the concrete slab is poured on-site; this solution is not very suitable for private individuals, mainly because of its weight, which a detached house can hardly support;
◦ or a reinforced aerated concrete slab, which comes in blocks assembled on site.
– Sheet steel:
◦ in a detached house, this technique is associated with a reinforced concrete slab ;
◦ an ideal solution in steel-framed houses.
– Wood, or wood derivative. The support, carried by a rigid and solid structure made of wood or masonry, can be in:
◦ solid wood;
◦ plywood designed for outdoor use;
◦ water-repellent treated particleboard.
Properly calculate the slope of a flat roof
A flat roof does not mean a completely flat roof. Indeed, if a slight slope is not provided, rainwater:
– is not evacuated;
– then stagnates on the surface of the flat roof.
Therefore, depending on the surface area, a slight slope of between 1 and 5% should be applied.
Here again, the methods vary according to the type of roof and its size:
– Inaccessible flat roofs have a slope of about 1%.
– Accessible flat roofs have a slope of 1.5% to 2%.
– Small flat roofs are slightly domed. The centre is the highest point.
– Large flat roofs are slightly sloped. The slope never exceeds 5%.
Good to know: for flat roofs with masonry support, a slope can be created with a layer of concrete or mortar poured with a slight inclination.
In all cases, drainage holes are installed at the bottom of this slope to evacuate rainwater, and downpipes carry the water to the bottom of the house.
Insulating a flat roof
Insulating the flat roof is mandatory and indispensable to:
– ensure thermal comfort in winter and summer;
– avoid energy losses as much as possible;
– protect the support of the flat roof and the house’s structure against big temperature changes.
As heat rises naturally, the roof is one of the sensitive points of the house.
Good to know: 30% of energy loss is through the roof in a poorly insulated house.
Insulation materials for the flat roof
A flat roof can be insulated with different materials:
– expanded polystyrene (EPS);
– mineral wool: rock wool and glass wool;
– expanded perlite;
– cellular glass;
– rigid polyurethane foam;
– expanded clay.
Choosing the right insulation for the flat roof
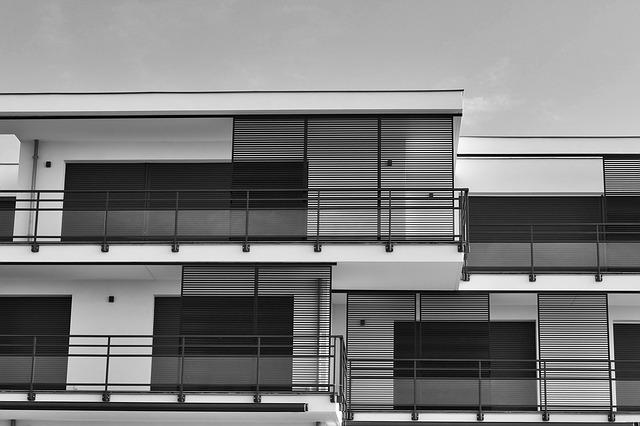

The choice of insulation depends on the characteristics of the roof to be suitable and therefore effective. Thus, it is necessary to take into account mainly:
– the type of flat roof: accessible or inaccessible.
– the type of support:
– masonry;
◦ sheet steel;
◦ wood.
– the type of protection that will be applied last (the roofing).
In addition, another constraint must be taken into account when choosing insulation for a flat roof: the compressive strength, classified from A to D, respectively from the least to the most resistant.
In contrast to sloped and rounded roofs, a flat roof cannot be insulated from the inside. According to the trade rules, it must be protected from the outside. The insulation is therefore located above the vapour barrier.
Possible openings
Due to its particular shape, the flat roof can only accommodate certain types of openings.
3 openings for the flat roof
Indispensable to let the sun penetrate and sometimes ventilate, there are three types of openings in flat roofs:
– The glass paving stone:
◦ glass pavers are small glass cubes installed in the screed when it is poured;
◦ they allow light to enter but do not ventilate the room or allow you to see outside.
– The skylight is:
◦ a window, often opaque, sometimes openable with a cable, and generally placed on the roof to take advantage of the zenithal lighting;
◦ a solution mainly used in industrial buildings.
– The roof window:
◦ these are the same roof windows as for sloping and rounded roofs; the only difference is that the minimal slope is compensated by sloping support, so that water does not stagnate on the window;
◦ the roof window, therefore, protrudes from the flat roof.
Waterproofing of the flat roof: the final protection
The waterproofing layer and other elements of the flat roof must be protected:
– from the effects of heat and cold;
– from the movement of people for roof maintenance.
This is done by applying a final layer called protection.
Different types of protection
The protection can be of several types:
– Furniture protection: composed of aggregates, for example, gravel.
– The rugged protection: a cast screed, laying a pave with a floor covering (self-locking paving stones or on blocks).
Guardrails for flat roofs
The protection of the flat roof is subject to some regulation that requires installing a guardrail.
Good to know: even so-called inaccessible flat roofs require a guardrail.
Hope this post will help you determine whether the flat roof is for you. Please remember to share your experience in the comments below.